Completeness
Completeness check is used to identify NULL values and treat specified values (like empty strings, white spaces, or fixed strings) as NULL. This allows users to enforce completeness data quality rules without writing any expressions.
Steps
- Navigate to the Checks tab of the Validation Rule.
- Click edit ✏️ button to rename the Check which is by default Chk_[Sequential_Number].
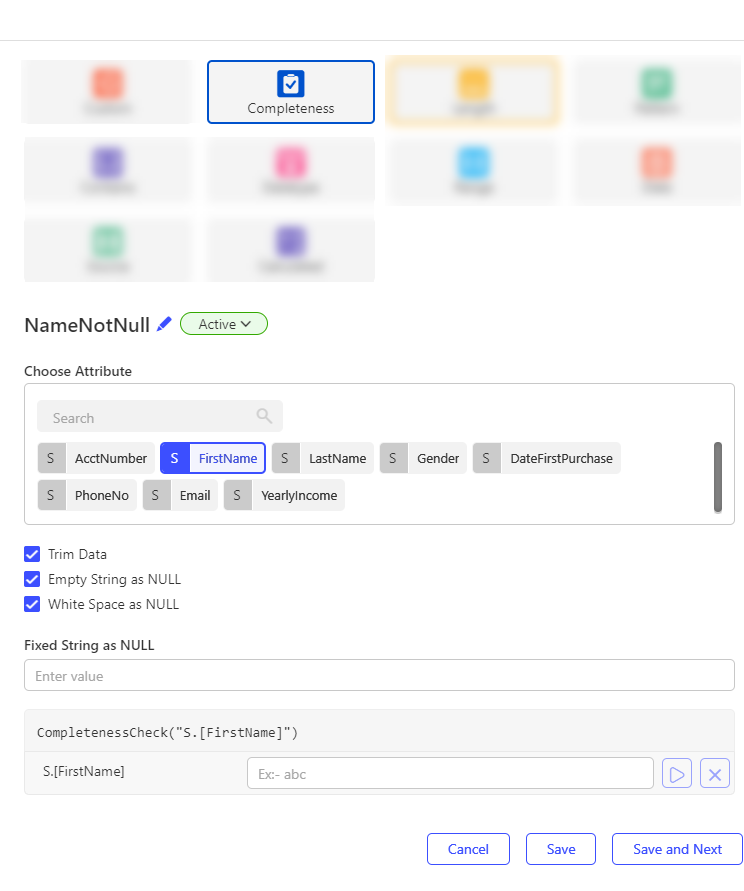
- Select Add, then choose Completeness.
- Search and select the column to perform the NULL check on.
- Configure the following optional setting:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Trim Data | If enabled, the engine will trim trailing/ leading spaces before applying the check. |
| Empty String as NULL | If enabled, the engine will treat an empty value ("") as NULL. |
| White Space as NULL | If enabled, the engine will treat a white space (" ") as NULL. |
| Fixed String as NULL | Specify a value to be treated as NULL. Only one fixed string can be added. Example: "NA" can be treated as NULL. |
- Use the test feature to validate the check logic without running the full rule. Enter sample input values in the text fields and click the Play button to view the output.
- Optionally, provide a Check Description to explain the purpose and business logic.
- Optionally, tag a Data Quality Dimension to the check.
- Finalize the check by selecting one of the following options:
- Cancel – Discard the check.
- Save – Save the check and close the configuration window.
- Save and Next – Save the current check and proceed to create a new one.
Output
- true – Any value that is NOT NULL.
- false – Any NULL value, including:
Empty strings (if configured).
White spaces (if configured).
Specified fixed string (if provided).
note
This check is currently supported only for columns with String datatype.
A single check can be applied to only one attribute. To validate multiple attributes, create separate Completeness checks for each.