Script
The Script Rule allows users to write custom Groovy Script to execute any pre-processing or post-processing tasks, and achieve end-to-end testing without leaving the iceDQ platform.
Use Cases
Here are some scenarios where a script rule can be used:
- Execute DDL/ DML statements to create test data
- Retrieve parameter value from a database and execute the Rule by passing the same value
- Clean up an incoming feed file to remove any unnecessary data or formatting
Components
There are three different components in a script rule: Overview, Connection and Script.
Overview
Users can provide Rule name, description, critical, and other metadata information to capture the logical definition of the Rule. Below are the properties that a user can set in the Advance Settings section.
| Property | Description | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Specify the default file that will be used to read parameter keys and values |
Connection
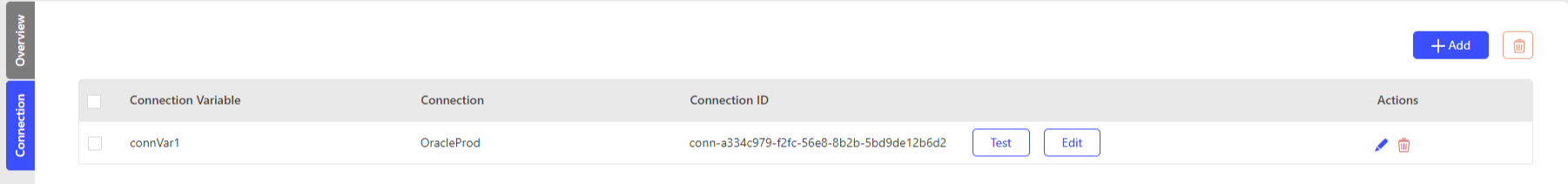
Users can add connection variables and choose a database connection as a value. Using the connection variable in the script rule enables the user to pass the connection as a value during runtime.
Script
This is a Groovy Script editor where users can write the script code and test it. Users can import pre-built Java libraries or custom libraries by writing an import statement, define variables, call Groovy functions, or use iceDQ built-in functions to perform the required task.
Exit Code
As the Script Rule is not evaluating any data, it does not have any Result Type for the engine to calculate the Exit Code. So the user must provide a Return statement to specify the Exit Code of the Script Rule.
| Return Statement | Status | Note |
|---|---|---|
| return "0"; | Success | The Script rule exit code is 0. |
| return "100"; | Failure (Warning/ Critical/ Blocker) | The Script rule exit code is greater than 100. |
| return "-150"; | Error | The Script rule exit code is less than -150. |
If there is an error in the Script, or the rule/workflow triggered from the Script errors out, then the Script will capture that Negative exit code.
Sample Code Snippets
Importing Libraries
Users can import pre-built Java libraries or custom libraries by writing an import statement at the top of the Script, as shown below.
import java.time.LocalDate
Define Variables
Users can define variables by using a specific datatype or by using def keyword.
def myNumber = 1000;
def messageVar = 'Today\'s date is ';
def tDate = LocalDate.now();
def sql = """ SELECT ID, NAME
FROM TABLE
WHERE ID = 1""";
Print Statement
Users can use the wrapper function to capture print statements to the log file
Function:
- instanceLog.info(String info)
Arguments:
- info: The content of the print statement.
Exception:
- Throws no exception.
instanceLog.info(" Today\'s date is " + tdate);
instanceLog.info(" $messageVar $tDate ");
Execute SQL Query
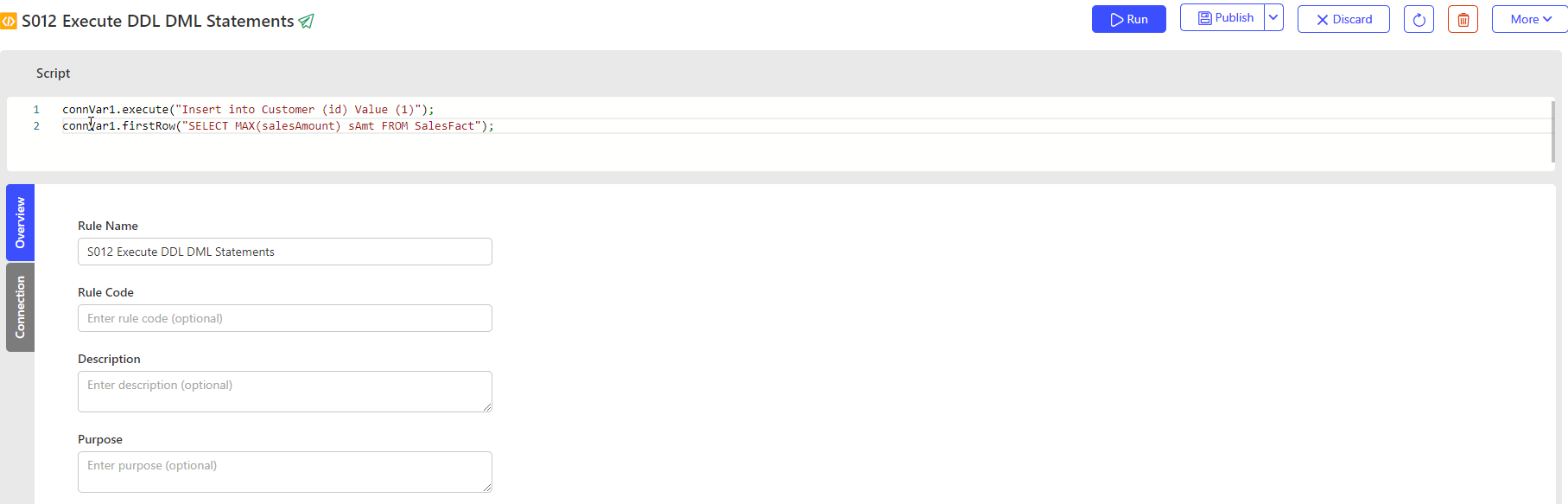
Apache Groovy allows users to interact with a database using Groovy SQL. The user has to create a connection (ZenCycleDemo) to the database and pass the connection as a value to the connection variable (connVar1) in the Script Rule. We have encapsulated the database connectivity so that users don't have to write code for the same. Users can call any Groovy database function, as shown below.
Function:
- DBConnectionName.execute(String sql)
Arguments:
- DBConnectionName: Connection variable used in script rule.
- sql: The SQL to execute.
Returns:
- true if the first result is a ResultSet object.
- false if it is an update count or there are no results.
Exception:
- Throws SQL execution if a database error occurs.
connVar1.execute("Insert into Customer (id) Value (1)");
connVar1.firstRow("SELECT MAX(salesAmount) sAmt FROM SalesFact");
Function:
- DBConnectionName.firstRow(String SQL)
Arguments:
- DBConnectionName: Connection variable used in script rule.
- sql: The Select statement to execute.
Returns:
- a GroovyRowResult object or null if no row is found.
Exception:
- Throws SQL execution if a database error occurs.
defrowResult = connVar1.firstRow (” SELECT COUNT(*) SCOUNT FROM CUSTOMER_CHECK”);
assert rowResult.SCOUNT == 0
Function:
- DBConnectionName.call(String SQL)
Arguments:
- DBConnectionName: Connection variable used in script rule.
- sql: The stored procedure to execute.
Returns:
- the number of rows updated or 0 for SQL statements that return nothing.
Exception:
- Throws SQL execution if a database error occurs.
connVar1.call(“BEGIN UPDATE_EMPLOYEES(3,100000); END;”);
Execute Rule/Workflow
Users can use the wrapper function to execute rule/workflow.
Function:
- workflow.execute(String objectId)
Arguments:
- objectId: The ruleId or workflowId.
Returns:
- Returns the Exit Code of the Rule/workflow as a String.
Exception:
- Throws a negative Exit Code, If objectId is invalid or objectId execution returns an error.
def ruleResult = workflow.execute(rule-179ed4c6-8278-5610-995a-1d87ce39ade3)
if (ruleResult.toInteger() > 0 )
{ resultMessage = "Rule is a Failure"; }
else
{ resultMessage = "Rule is a Success"; }
Execute Workflow Overriding Connections
Users can use the wrapper function to execute workflow overriding the connections.
Function:
- workflow.execute(String objectId, String overrideString)
Arguments:
- objectId: The workflowId.
- overrideString: The JSON string.
JSON Attributes:
- overrideSequence: The sequences to be overridden.
- Values: all, selected
- overrides: The list of entities to be overridden.
- sequence: The seq no in workflow.
- connection: The list of connections to be overridden.
- type: Source/target connection.
- find: Original connection.
- replace: Override connection.
- connection: The list of connections to be overridden.
{
"overrideSequence": "all",
"overrides": [
{
"connection": [
{
"type": "source",
"find": "connectionID",
"replace": "connectionID"
},
{
"type": "target",
"find": "connectionID",
"replace": "connectionID"
}
]
}
]
}
{
"overrideSequence": "selected",
"overrides": [
{
"sequence": [
3,
5
],
"connection": [
{
"type": "source",
"find": "connectionID",
"replace": "connectionID"
},
{
"type": "target",
"find": "connectionID",
"replace": "connectionID"
}
]
}
]
}
Returns:
- Returns the Exit Code of the Rule/workflow as a String.
Exception:
- Throws a negative Exit Code, If objectId is invalid or objectId execution returns an error.
def overrideString = '''{
"overrideSequence": "all",
"overrides": [
{
"connection": [
{
"type": "source",
"find": "conn-acf88d84-e55e-5bf0-a3e4-430edc624b",
"replace": "conn-f08ce866-0690-5f94-86b9-7d48bfd0fb07"
},
{
"type": "target",
"find": "conn-acf88d84-e55e-5bf0-a3e4-430edc624b",
"replace": "conn-f08ce866-0690-5f94-86b9-7d48bfd0fb07"
}
]
}
]
}'''
def objectId = 'wkfl-40b9d0c3-f48c-5c3f-a4b7-0cd9e207cb74'
def result = workflow.execute(objectId, overrideString)
instanceLog.info("Exit Code: "+ result.exitCode)
return result.exitCode;
"overrideSequence": "selected",
"overrides": [
{
"sequence": [
3,
5
],
"connection": [
{
"type": "source",
"find": "conn-acf88d84-e55e-5bf0-a3e4-430edc624b",
"replace": "conn-f08ce866-0690-5f94-86b9-7d48bfd0fb07"
},
{
"type": "target",
"find": "conn-acf88d84-e55e-5bf0-a3e4-430edc624b",
"replace": "conn-f08ce866-0690-5f94-86b9-7d48bfd0fb07"
}
]
}
]
}'''
def objectId = 'wkfl-40b9d0c3-f48c-5c3f-a4b7-0cd9e207cb74'
def result = workflow.execute(objectId, overrideString)
instanceLog.info("Exit Code: "+ result.exitCode)
return result.exitCode;
Considerations
- If there is an error in the Script, the Exit Code will be less than 0 (negative). And if the Rule/ Regression Pack triggered from the Script errors out, then the Script will capture that Negative exit code.
- Script rule is used to do a menial task. A custom script not written properly can consume all the memory and CPU and bring the server down.
- Database Connections created in the workspace can only be used in the script rule by passing them as values to Connection Variables.
- As of now, iceDQ supports adding only five connection variables.