Troubleshooting Checklist
Use this topic as a checklist for troubleshooting issues with the icedq app
Admin password
Admin Console password can be reset using below command
kubectl kots reset-password default
Check IP forwarding status
IP Forwarding is imptortant to run the installation and can be enabled by following procedure.
# Run follwing command to see the IP forwarding status
sudo sysctl net.ipv4.conf.all.forwarding
sudo sysctl net.ipv4.ip_forward
# If output of the abe command is 0 then IP forwading needs to be enabled by using below
sudo vi /etc/sysctl.conf
# Add or update below lines in sysctl.conf
net.ipv4.conf.all.forwarding=1
net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
# Save the changes and run below command to apply the changes permanently
sudo sysctl -p
Check containerd status
systemctl status containerd
Check Kubernetes configurations
Kubelet
# to check the kubelet status use
systemctl status kubelet
# to restart the kubelet use
systemctl restart kubelet
Cluster Node
# to check the node status use below, All nodes should show Ready in the STATUS column.
kubectl get nodes
# to restart the kubelet use
kubectl describe node NODENAME
Pods
# to check the pods that are not running
kubectl get pods -A | grep -v Running | grep -v Completed
# Check pod logs for any issue
kubectl logs --all-containers PODNAME -n NAMESPACE -f
# Describe pod
kubectl describe pod PODNAME -n NAMESPACE
# Check errors in events
kubectl get events --sort-by=.metadata.creationTimestamp
Deploys
# Get all deploys
kubectl get deploy -A
# Scale down deployments
kubectl scale deploy DEPLOYNAME --replicas=0
# Scale UP deployment
kubectl scale deploy DEPLOYNAME --replicas=1
Statefulset
# Get all deploys
kubectl get sts -A
# Scale down deployments
kubectl scale sts STSNAME --replicas=0
# Scale UP deployment
kubectl scale deploy STSNAME --replicas=1
Velero
velero describe backup BACKUPNAME --details
velero describe restore RESTORENAME --details
velero logs restore RESTORENAME
kubectl logs PODNAME -n velero -f
kubectl get podvolumebackup -n velero | grep Failed
kubectl get backuprepositories -n velero
kubectl delete backuprepositories -n velero --all
kubectl delete podvolumebackup -n velero --all
kubectl delete backup -n velero --all
AWS S3 Policy for storage
cat > velero-policy.json <<EOF
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ec2:DescribeVolumes",
"ec2:DescribeSnapshots",
"ec2:CreateTags",
"ec2:CreateVolume",
"ec2:CreateSnapshot",
"ec2:DeleteSnapshot"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:DeleteObject",
"s3:PutObject",
"s3:AbortMultipartUpload",
"s3:ListMultipartUploadParts"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::${BUCKET}/*"
]
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:ListBucket"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::${BUCKET}"
]
}
]
}
EOF
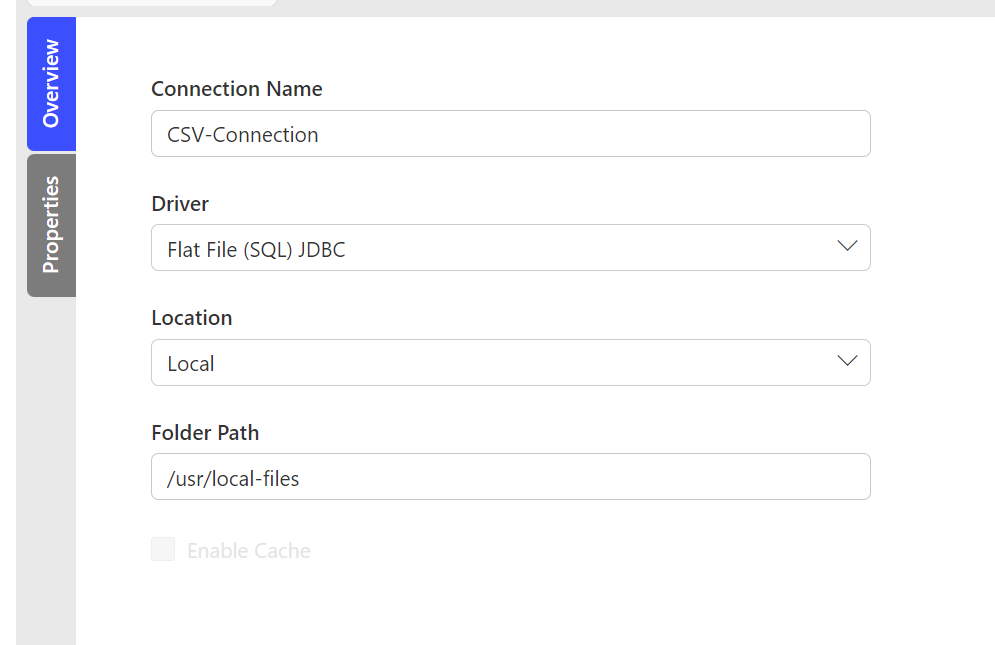
Upload files on kubernetes cluster
-
Log in to the VM or Jumpbox
-
Create new directory example -
mkdir csv -
Copy file from local computer to VM's local path
/home/ubuntu/csv/ -
Identify the pod name by running below command
kubectl get pods -n default | grep "icedq-connection" | awk '{print $1}' | grep -m 1 "icedq-connection"
# You will see output like below
icedq-connection-5d9dd8758-w7cdp 1/1 Running 11 (78m ago) 18d
icedq-connection-ui-7cc5c46c56-lwppj 1/1 Running 10 (16h ago) 18d
- Run command to copy files from local csv directory to pods volume.
kubectl cp <local-directory-path> <namespace>/<pod-name-from-step-4>:/usr/local-files
# example
kubectl cp /home/ubuntu/csv/ default/icedq-connection-5d9dd8758-w7cdp:/usr/local-files
- Configure the path in NextGen app